Drug development process — from the start

According to Fredrik Sundberg, PhD, global director of strategic customer relations at GE Healthcare, Uppsala, Sweden, “The key to successfully launch a drug product on the market is to thoroughly understand, early in the drug development process:
- The mechanism of action of the drug candidate
- Molecular stability of the candidate during development and manufacturing
- The influence the process parameters will have on the product’s quality with respect to patient safety.”
Sundberg works closely with the biopharma industry to improve current workflows associated with discovery, development, and manufacturing quality control by providing various types of bio-analytical solutions support. According to him, understanding of the process is the key to success.
“It’s essential in the design of the process itself, candidate selection, and recognising the manufacturability and scalability of these candidates. Most of the impurities, such as DNA residue, host cell proteins (HCPs), additives, etc, can be minimised if you make the right decisions early on, and you can hone in on the best combination of biological activity, biophysical properties, sequence and epitope diversity in the search and development of your leads.”
Proper process understanding allows researchers to critically identify factors that impact the drug substance and product and minimise or maintain them at approved levels. This way, researchers can achieve the desired therapeutic outcome without compromising patient safety or introducing dangerous side effects. It is also essential to demonstrate this understanding in submissions to the health authorities.
Monitoring critical process parameters for a well-characterised product
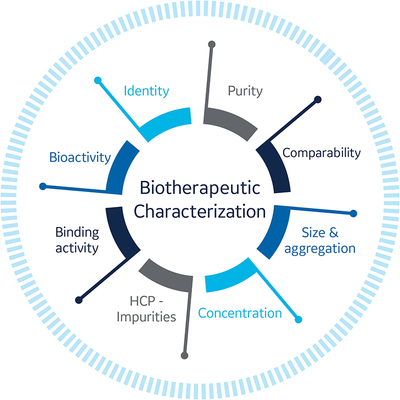
Both upstream processing and downstream processing can affect critical quality attributes of the drug molecule under development (Fig 1). These effects can result in process-related impurities (eg, DNA residue, HCPs), product impurities (eg, aggregates like dimers, oligomers), and post-translational modifications (eg, glycosylation and conformational changes that can affect critical binding epitopes).
To establish a well-characterised biological product, many aspects of the drug substance and product must be monitored including:
- Charge and molecular weight distribution
- Primary/secondary/tertiary structures
- Mechanistic pathways
- Biological activity in terms of in vivo potency and binding affinity
Benefits of SPR technology and its role in the biopharma industry
SPR technology can be used to study molecular interactions in real time with label-free detection. The major advantage of the technology is that it provides a wealth of information related to affinity, kinetics, concentration, thermodynamics, bio-similarity, specificity and selectivity.
SPR is a powerful tool for understanding structure-function relationships and can be used from early basic research all the way through to development and manufacturing as a platform technology in the biopharma industry.
“In manufacturing, using sensorgram comparison provides a rapid ID of the drug-target interaction, and the overall SPR analysis provides more information faster, finishing an assay in 10 minutes versus several hours,” says Sundberg. “With SPR technologies, you can detect subtle changes very early on and take corrective action in due time to mitigate potential issues.”

Want to learn more about SPR? Read the full blog here, or join us for the free Biacore Day to meet Fredrik Sundberg and others from our team by registering at https://shop.monash.edu/fragment-based-drug-design-down-under-2019.html.
Personality influences the expression of our genes
An international research team has used artificial intelligence to show that our personalities...
Pig hearts kept alive outside the body for 24 hours
A major hurdle for human heart transplantation is the limited storage time of the donor heart...
Breakthrough antibiotic for mycobacterial infections
The antibiotic candidate, named COE-PNH2, has been optimised to target Mycobacterium...







