Lab-on-a-chip analyses health of white blood cells
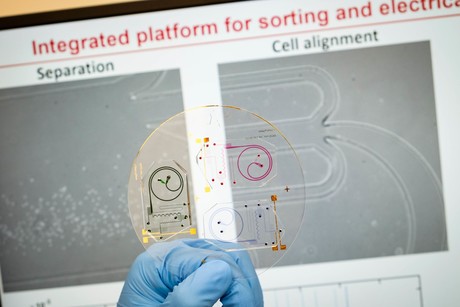
Scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Assistant Professor Hou Han Wei and Assistant Professor Holden Li, have developed a lab-on-a-chip system that can identify the health aspects of a person’s immune system from a drop of their blood, within minutes.
Using a combination of microfluidics and electrical sensors, the chip was able to detect differences in the electrical properties of white blood cells taken from healthy and diabetic patients. The prototype device and the engineering principles behind it have been reported in the journals Lab on a Chip and Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
If the invention proves successful in further laboratory and clinical assessments, it could be turned into a portable device suitable for family clinics and polyclinics. Indeed, the proof-of-concept device may one day help doctors to quickly gain insight into a person’s immune system, and spot early signs of inflammation and infection that could signal the need for further in-depth tests.
White blood cells form a significant part of the body’s immune system, with a key type known as neutrophils serving as the first line of defence when infection or inflammation strikes. Asst Prof Hou said the chip detects electrical differences between a healthy white blood cell and an unhealthy one — abnormal white blood cells have been reported as an early biomarker for increased risk of cardiovascular diseases and also suggest ongoing inflammation.
Using tiny microscopic channels, the chip first physically separates the various blood cells by size into the different outlets, like a coin-sorting machine. The isolated white blood cells are then run through a special channel where electrical impedance is measured for each cell at a very high speed (hundreds of cells per second). The electrical impedance of an abnormal cell is usually higher than the impedance of a healthy cell, given as an abnormal cell is larger in size and has different membrane properties.
“Our chips can isolate thousands of white blood cells from a single drop of blood and, within minutes, tell if these cells are electrically different from normal, which would be an indicator of whether there is a health issue to be further investigated,” Asst Prof Hou said.
“More importantly, our process also does not use any chemical biomarkers or antibodies, which makes the assay cheap, easy to use, and … we can do further analysis on the same white blood cells we have already run through the chip.”
Asst Prof Li said that the material used to make the lab-on-a-chip is a common medical-grade polymer that is easily manufactured using existing machinery, and can be made into a desktop-sized machine for use in clinics.
“Our chip was designed for easy scale-up by companies, with an integrated system built from electronic components available on the market,” he said. “Moving forward, we are looking to commercialise the technology with an industry partner, as we see that there are market demands for a point-of-care device for doctors and as laboratory equipment for the study of neutrophils and drug screening.”

As immune health is often implicated in cardiovascular diseases, the scientists say that their device can potentially be an additional screening tool for doctors to use for early detection of cardiovascular diseases, which accounted for 30.1% of all deaths in Singapore in 2017. Diabetes is another serious health problem, which affects about 10% of the world’s population — and NTU’s Professor Bernhard Boehm noted that many diabetic patients are also susceptible to chronic infections due to disease affecting the performance of the immune system.
“There are a number of limitations to using conventional diagnostic markers for patients with clinical suspicion of infection,” said Prof Boehm, who was not involved in the study. “In particular, there is a need to improve early diagnosis of bacterial infections and to provide guidance for antibiotic therapy.
“Therefore, a test system that can rapidly guide decisions about initiation of specific therapies would be of great help in a clinical setting. However, this will need in the near future, randomised controlled clinical trials to provide formal proof that the novel test system is superior to the currently used conventional diagnostic procedures.”
The device could also be useful for the study of NETosis, a newly discovered defence mechanism in the field of immunology. During NETosis, neutrophils spit out DNA strands that trap bacteria and viruses, much like a spider’s web, to impede their movements and to kill the trapped pathogens. However, too much NETosis also slows down wound healing in diabetes.
NTU NETosis expert Assistant Professor Christine Wong, who was not involved in this study, said the most widely adopted methodology for studying NETosis propensity currently is real-time imaging or microscopy of fixed neutrophils. However, it is a laborious process for researchers to isolate the neutrophils for microscopy without affecting their native baseline state, and not influence experimental results.
“The new device by Asst Prof Hou and Asst Prof Li may enable rapid and non-biased NETosis experiments and quantification, which will be especially useful for drug screening ex vivo,” Asst Prof Wong said.
“If the device can be modified to measure NETosis in mouse neutrophils, this would be delightful news for researchers using mouse models, as low neutrophil yield is a common obstacle in mouse neutrophil isolation due to the smaller blood volume available in mice and their lower myeloid cell ratio when compared to humans.”
Asst Prof Wong added that while the new device is unlikely to replace microscopy experiments, in particular when visualisation of cellular components during the NETosis process is the subject matter, the resources saved from NET quantification could be diverted to those investigations.
The scientists are currently doing more research on the various electrical impedance levels and what each of them signifies, so as to build a sort of reference library for an automated analysis, and will be working with doctors to test their prototype in the clinical setting.
Please follow us and share on Twitter and Facebook. You can also subscribe for FREE to our weekly newsletters and bimonthly magazine.
Best practices for safe centrifugation in the laboratory
The majority of all centrifuge accidents are understood to result from user error. These tips...
Nature-inspired filtration system recovers critical resources
A filtration system that can recover untapped critical resources such as copper and lithium from...
Optimising food and beverage testing with laboratory equipment
In the food and beverage industry, laboratories must balance precision, speed and compliance to...





